Spasticity, a motor disorder characterized by a velocity-dependent increase in muscle tone, often results from
damage to the brain or spinal cord. This condition leads to stiff and difficult movements, significantly impacting
daily life. This blog post explores how EMG biofeedback, a powerful tool in physiotherapy, offers a promising
solution for regaining control and improving quality of life. We delve into the evidence-based mechanisms behind
EMG biofeedback, examining its benefits and practical applications in helping patients recover movement after spasticity.
Understanding Spasticity: Causes, Symptoms, and Impact on Movement
Understanding the basics of spasticity is crucial for effective management. Spasticity often results from damage
to the central nervous system, such as stroke, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, and traumatic brain injury. These
conditions disrupt the normal pathways that control muscle tone and movement, leading to spasticity.
The symptoms of spasticity vary widely, ranging from mild muscle stiffness to severe, uncontrollable muscle
spasms. This can lead to difficulties with walking, grasping objects, and performing other everyday tasks. The
impact on movement can be profound, affecting a person's independence, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
EMG biofeedback offers a targeted approach to address these challenges by helping patients regain control over
their muscles.
EMG Biofeedback for Spasticity: A Physiotherapy Solution
for Movement Recovery
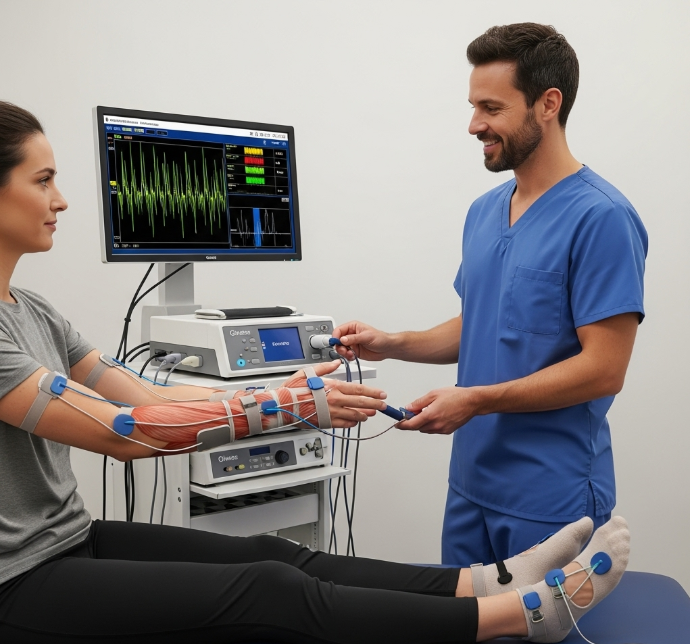
EMG biofeedback utilizes sensors to detect and display the electrical activity of muscles. By placing sensors on
the skin over specific muscles, the PhysioEMG device detects the electrical signals produced during muscle
contraction and relaxation. This information is then displayed visually or audibly, allowing patients to become
aware of their muscle activity in real-time.
This real-time feedback is key to retraining your muscles. Patients learn to identify when their muscles are tense
or relaxed and can then practice techniques to consciously control their muscle activity. Over time, this can lead
to improved motor control, reduced spasticity, and enhanced functional abilities. EMG biofeedback is often used
in conjunction with other physiotherapy interventions, such as stretching, strengthening exercises, and functional
training, to maximize its benefits. In physical therapy, EMG biofeedback in physical therapy is becoming a key
integrative approach to muscle rehabilitation.
1. Relaxing Spastic Muscles and Activating Weak Muscles with
EMG Biofeedback
One of the primary benefits of EMG biofeedback is its ability to help patients relax spastic muscles. By providing
real-time feedback on muscle activity, individuals can learn to consciously reduce the tension in their muscles.
This is particularly helpful for those with spasticity, as it allows them to break the cycle of muscle tightness and
spasm.
Simultaneously, EMG biofeedback can also be used to activate weakened muscles. Often, spasticity is accom-
panied by weakness in opposing muscle groups. By focusing on activating these weak muscles, patients can
improve muscle balance and coordination. The PhysioEMG device provides targeted feedback, helping patients
to engage the correct muscles and increase their strength.
2. Enhancing Motor Control and Retraining Neural Pathways
with EMG Biofeedback
EMG biofeedback plays a vital role in enhancing motor control by retraining neural pathways. Spasticity often
disrupts the normal communication between the brain and muscles. Through consistent use of EMG biofeedback,
patients can re-establish these connections, improving their ability to control movement.
The process involves consciously attempting to perform specific movements while receiving real-time feedback
from the PhysioEMG device. This helps the brain to relearn the correct patterns of muscle activation, leading
to smoother, more coordinated movements. This approach aligns with principles of neuroplasticity, the brain's
ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections.
3. Increasing Range of Motion for Enhanced Mobility with EMG
Biofeedback
Spasticity often leads to a restricted range of motion, making it difficult to perform everyday activities. EMG
biofeedback can help to increase range of motion by reducing muscle tightness and improving joint flexibility. As
patients learn to relax their spastic muscles, they can gradually increase their range of motion through targeted
exercises and stretches.
The PhysioEMG device provides valuable feedback during these exercises, ensuring that patients are using the
correct muscles and avoiding compensatory movements. This can lead to more effective stretching and improved
joint mobility, ultimately enhancing overall mobility and function.
4. Alleviating Spasticity-Related Pain Through Muscle Relaxation
with EMG Biofeedback
Pain is a common symptom associated with spasticity. Chronic muscle tightness and spasms can lead to
significant discomfort and reduced quality of life. EMG biofeedback can help to alleviate spasticity-related pain
by promoting muscle relaxation. In real therapy settings, EMG biofeedback has shown impressive outcomes in
treating chronic musculoskeletal pain, where patients learn pain management by controlling muscle tension.
By learning to consciously relax their muscles, patients can reduce the pressure on joints and nerves, leading
to pain relief. The PhysioEMG device provides a visual or auditory representation of muscle tension, allowing
patients to monitor their progress and make adjustments as needed. This can be a powerful tool for managing
chronic pain and improving overall well-being.
5. Enhancing Functional Abilities in Daily Life with Improved
Movement
The ultimate goal of spasticity treatment is to improve functional abilities and enhance independence in daily life.
EMG biofeedback can contribute significantly to this goal by improving movement control, reducing pain, and
increasing range of motion. As patients regain control over their muscles, they can perform everyday tasks with
greater ease and confidence.
Whether it's reaching for objects, walking, or dressing, improved movement can have a profound impact on a
person's quality of life. EMG biofeedback in physical therapy is becoming a key integrative approach to muscle
rehabilitation, combined with other physiotherapy interventions, can help patients achieve their functional goals
and live more fulfilling lives.
6. Personalized EMG Biofeedback Treatment Tailored to Individual
Needs with PhysioEMG
One of the key advantages of EMG biofeedback is its ability to be personalized to meet the unique needs of each
patient. The PhysioEMG device empowers your therapist to create a treatment plan that's uniquely designed for
you, targeting the specific muscles and movements that matter most to your recovery.
During a biofeedback session, the therapist can adjust the sensitivity of the sensors, the type of feedback
provided, and the specific exercises performed. This ensures that the treatment is tailored to the patient's current
abilities and progress. This personalized approach maximizes the effectiveness of EMG biofeedback and helps
patients achieve optimal outcomes.
7. Objective Measurement and Progress Tracking with PhysioEMG
in Physiotherapy
EMG biofeedback provides objective data that can be used to track progress and measure the effectiveness of
treatment. The PhysioEMG device records muscle activity during each session, providing quantifiable data that
can be compared over time.
This data can be used to monitor changes in muscle tension, motor control, and functional abilities. By tracking
progress objectively, therapists can make informed decisions about treatment adjustments. This objective
measurement also provides motivation for patients, as they can see tangible evidence of their improvement.
Applications in neuromuscular rehabilitation are vast, underlining EMG biofeedback’s versatility in boosting
patient engagement and response.
EMG Biofeedback for Spasticity: Helping Patients with Stroke,
Cerebral Palsy, MS
EMG biofeedback has proven to be a valuable tool in managing spasticity associated with various neurological
conditions. For stroke patients, it aids in regaining motor control and improving muscle function in affected limbs.
In individuals with cerebral palsy, EMG biofeedback assists in muscle re-education and enhancing movement
coordination. Similarly, patients with multiple sclerosis can benefit from EMG biofeedback to reduce muscle
stiffness and improve mobility. EMG biofeedback is extensively employed to assist patients with conditions like
cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis, where muscle control is imperative.
The versatility of EMG biofeedback makes it a suitable intervention for a wide range of patients experiencing
spasticity. By targeting specific muscle groups and providing real-time feedback, it helps individuals regain control
over their movements and improve their overall quality of life.
EMG Biofeedback Techniques in Physiotherapy for Spasticity
Several EMG biofeedback techniques are employed in physiotherapy for spasticity management. One common
approach involves surface EMG, where sensors are placed on the skin to detect muscle activity. Another
technique is intramuscular EMG, which involves inserting fine-wire electrodes into the muscle to record electrical
signals.
Regardless of the technique used, the goal is to provide patients with real-time feedback on their muscle activity,
allowing them to learn how to consciously control their muscles. This may involve techniques such as muscle
relaxation exercises, reciprocal inhibition (contracting the opposing muscle group to relax the spastic muscle),
and motor imagery (mentally rehearsing movements). Visual or auditory representations of muscle activity help
pinpoint areas needing enhancement, focusing and enriching your rehabilitation journey. The choice of technique
depends on the individual patient's needs and the specific muscles being targeted. Sometimes, techniques like
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) are used alongside EMG biofeedback to enhance the effects.
Conclusion
EMG biofeedback is a transformative element in physical therapy, empowering you to precisely manage and
enhance your neuromuscular recovery. Whether you are regaining strength post injury or overcoming neuromus-
cular challenges, incorporating this technology has shown unequivocal benefits. It offers a non-invasive, drug-free
approach to managing spasticity and improving movement. By providing real-time feedback on muscle activity,
EMG biofeedback empowers patients to consciously control their muscles, leading to improved motor control,
reduced pain, and enhanced functional abilities.