Neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage, can cast a long shadow over a person's life. This condition
manifests in a range of debilitating symptoms, including sharp, shooting pain, persistent numbness, tingling sensations,
and weakness, often affecting the hands and feet. These symptoms can make everyday activities a struggle, impacting
mobility, sleep, and overall well-being. Fortunately, there's hope. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, or TENS,
offers a non-invasive approach to pain relief that can be integrated into a comprehensive physiotherapy plan.
This blog post explores how TENS, specifically using the Axonease device, helped one patient regain control over their life
and find relief from debilitating neuropathy symptoms. We'll delve into the specifics of their journey, highlighting the measurable
improvements achieved through personalized TENS therapy and emphasizing the crucial role of professional
physiotherapy guidance.
Understanding TENS for Neuropathy Pain Relief
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) is a non-invasive pain management technique that utilizes
low-voltage electrical currents. These currents are delivered through electrodes placed on the skin, targeting
specific nerve pathways. TENS works by blocking pain signals from reaching the brain, a process often explained
by the gate control theory of pain, and prompting the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers.
This dual action makes TENS a valuable tool in managing various types of pain, including that associated with
neuropathy. Different types of TENS units exist, including conventional, acupuncture-like, and burst modes, each
with specific applications.
The effectiveness of TENS depends on several factors, including the type and severity of neuropathy, the
individual's pain threshold, and the specific parameters of the TENS unit used. Parameters like pulse width,
frequency, and intensity can be adjusted to achieve optimal pain relief. Proper electrode placement is crucial for
effective treatment, as it directly influences the stimulation of targeted nerve pathways. It's crucial to consult with
a healthcare professional, particularly a physiotherapist, to determine if TENS is appropriate and to develop a
personalized treatment plan.
The Patient's Struggle with Neuropathy Symptoms
Our patient, Sarah, a 62-year-old retired teacher, had been living with peripheral neuropathy for several years.
Before the onset of neuropathy, Sarah was an active individual who enjoyed gardening, spending time with her
grandchildren, and volunteering at her local library. Her hobbies and social activities were central to her life,
providing her with joy and a sense of purpose. However, the onset of neuropathy gradually eroded her ability to
participate in these activities. Her symptoms included sharp, shooting pain in her feet, persistent numbness, and
a tingling sensation that made it difficult to walk and sleep. The constant discomfort and limitations significantly
impacted her daily activities and overall well-being. Simple tasks like walking to the mailbox, preparing meals, or
even getting dressed became major challenges.
Sarah's neuropathy had also taken a toll on her emotional well-being. The constant pain and limitations led to
feelings of frustration, anxiety, and isolation. She had tried various medications, but they provided only temporary
relief and often came with unwanted side effects. The side effects of the medications, such as drowsiness and
nausea, further limited her ability to enjoy her daily life. Sarah was seeking a more sustainable and holistic
approach to managing her neuropathy and reclaiming her life.
Personalized TENS Therapy Protocol with Axonease
Sarah's physiotherapy assessment revealed significant sensory deficits and pain upon light touch in her lower
extremities. Her muscle strength was also reduced, particularly in her ankles and feet. Based on these findings,
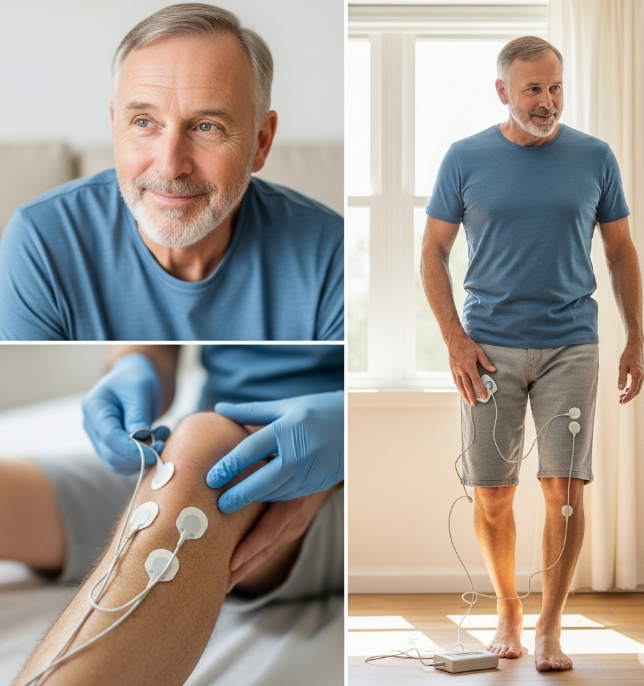
a personalized TENS therapy protocol was developed using the Axonease device. The Axonease was chosen
for its user-friendly interface, adjustable parameters, and ability to deliver targeted stimulation, making it easy for
Sarah's physiotherapist to tailor the treatment precisely to her needs and comfort level. The Axonease device, as
shown in the study, is a modern TENS device.
The TENS protocol involved placing electrodes on specific acupoints along Sarah's lower legs and feet, targeting
the affected nerve pathways. The frequency and intensity of the electrical stimulation were carefully adjusted to
achieve optimal pain relief without causing discomfort. Sarah received TENS therapy sessions three times a week,
each lasting for 30 minutes. In addition to TENS, her physiotherapy program included range-of-motion exercises,
muscle strengthening exercises, and sensory re-education techniques. The goals of physiotherapy in the acute
stage of peripheral neuropathy, such as reduction of pain, prevention of muscle atrophy, and maintenance of
range of motion, were effectively addressed through the combined approach of TENS and targeted exercises.
As Sarah progressed into the recovery stage, the physiotherapy interventions focused on muscle re-education,
strengthening, and sensory re-education, further enhancing her functional abilities.
How TENS Therapy Improved the Patient's Quality of Life: Measurable Results
After several weeks of consistent physiotherapy, Sarah experienced significant improvements
in her neuropathy symptoms and overall quality of life. Her pain levels decreased substantially, allowing her to
walk with greater ease and participate in more activities. The numbness and tingling sensations in her feet also
diminished, improving her sleep quality and reducing her anxiety.
The improvements were not only subjective but also measurable. Sarah's pain scores on a visual analog scale
(VAS) decreased from 7/10 to 3/10. Her walking speed and endurance also increased, as measured by a
timed walk test. Furthermore, she reported a significant improvement in her ability to perform daily activities,
such as dressing, bathing, and preparing meals. These improvements weren't just numbers; they represented
Sarah reclaiming her independence and rediscovering the joy in everyday activities. The combined approach of
TENS and targeted exercises effectively addressed the acute and recovery stages of peripheral neuropathy. The
long-term benefits of TENS therapy and physiotherapy for managing neuropathy include sustained pain relief,
improved mobility, and enhanced overall well-being.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Managing Neuropathy with TENS
While TENS can be a valuable tool for pain relief, it's essential to recognize that it's most effective when integrated
into a comprehensive physiotherapy program. Physiotherapists play a crucial role in assessing the individual's
condition, developing a personalized treatment plan, and monitoring progress. They can also provide guidance
on proper TENS unit usage, electrode placement, and stimulation parameters.
Physiotherapy interventions for pain relief in individuals with peripheral neuropathic pain include manual therapy
techniques like massage and joint mobilization, which can reduce pain and stiffness. Electrical stimulation, such
as TENS, provides additional pain relief. Education about pain mechanisms and self-management strategies
empowers patients to take control of their condition. Furthermore, targeted exercises help maintain muscle
strength, especially for those with motor neuropathy, improving mobility and independence. Physiotherapy is a
readily accessible and valuable resource for individuals seeking relief from neuropathy pain. Research suggests
that physiotherapy can be a valuable component of managing Neuropathy, though its efficacy can differ depending
on the specific type and cause. The role of physiotherapy extends beyond pain management; it also addresses
psychological factors, such as anxiety and depression, which often accompany chronic pain conditions.
Physiotherapists also play a vital role in preventing falls and improving balance in patients with
neuropathy, thereby enhancing their safety and independence.
Conclusion
Sarah's story exemplifies how TENS therapy, combined with expert physiotherapy, can significantly improve
the quality of life for individuals with neuropathy. By reducing pain, improving mobility, and enhancing overall
well-being, TENS can empower patients to regain control over their lives and pursue their passions. It's important
to remember that TENS is not a cure for neuropathy, but it can be a valuable tool for managing symptoms and
improving function.
If you or someone you know is living with neuropathy, consider exploring the potential benefits of TENS therapy
and physiotherapy. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if TENS is appropriate and to develop a
personalized treatment plan. Don't let neuropathy define your life – take proactive steps towards pain relief and
improved well-being. The future of TENS therapy and its role in managing chronic pain conditions looks promising,
with ongoing research exploring its potential in various applications.