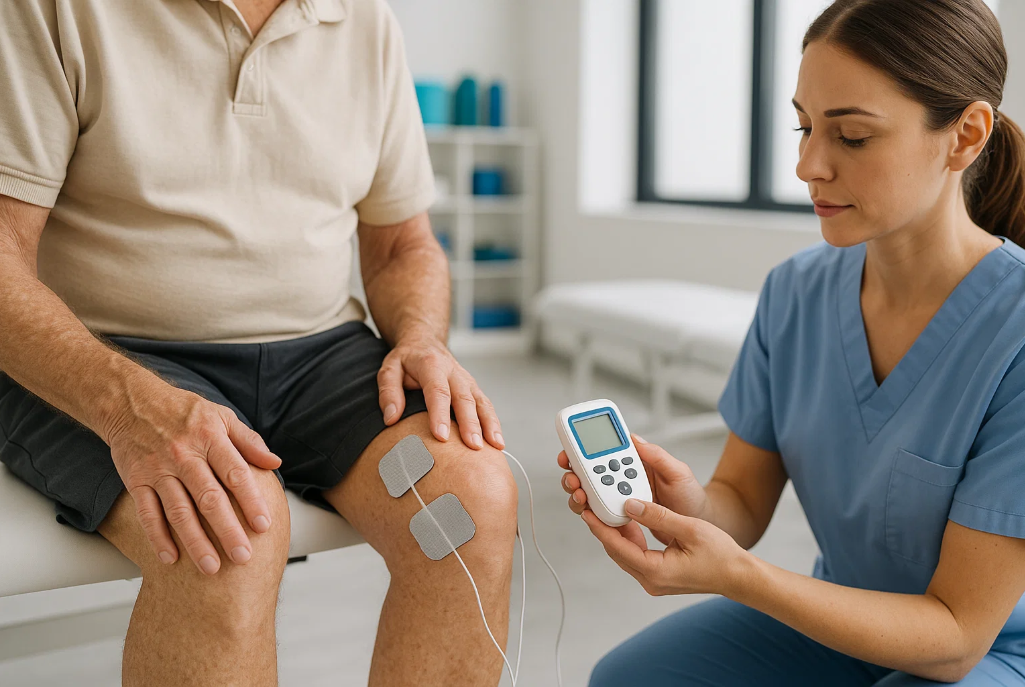
Arthritis, a condition characterized by joint inflammation, affects millions worldwide, significantly impacting their
quality of life. The global prevalence of osteoarthritis, a leading cause of disability, underscores the urgent need for
effective pain management strategies. The economic burden of arthritis is substantial, encompassing healthcare
costs and lost productivity. Beyond the physical symptoms, chronic pain and limited mobility can lead to fatigue,
sleep disturbances, and psychological distress, such as anxiety and depression. Managing arthritis effectively
requires a multidisciplinary approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
One such approach gaining recognition within physiotherapy is Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
(TENS). TENS offers a non-pharmacological path to pain relief, utilizing a small, portable device to deliver mild
electrical impulses through the skin. This stimulation interferes with pain signals sent to the brain and promotes
the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers. This blog post presents a detailed case study showcasing
the effective integration of TENS into a physiotherapy plan for managing arthritis pain. We will explore the
mechanisms of TENS, its application, and the outcomes observed in a patient with arthritis, emphasizing the
role of physiotherapy in optimizing its use.
Understanding TENS Therapy and Arthritis
TENS: A Non-Pharmacological Approach to Pain Relief
TENS, or Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, is a physiotherapy technique that utilizes a device to
deliver mild electrical impulses through the skin. This stimulation interferes with pain signals sent to the brain and
promotes the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers. The intensity and frequency of these electrical
impulses can be adjusted to suit individual needs and comfort levels. TENS units are portable and can be used
at home, providing a convenient way to manage pain throughout the day.
Different types of TENS, such as conventional, acupuncture-like, and burst, utilize varying parameters like fre-
quency and pulse width, influencing their mechanisms of action. Conventional TENS typically uses high-frequen-
cy, low-intensity stimulation to activate sensory nerves, while acupuncture-like TENS employs low-frequency,
high-intensity stimulation to trigger the release of endorphins. The gate control theory of pain explains how TENS
interacts with the nervous system. By stimulating the sensory nerves, TENS can "close the gate" to pain signals,
preventing them from reaching the brain. It's also important to acknowledge the placebo effect in TENS therapy,
where a patient's belief in the treatment can contribute to pain relief.
Arthritis: Types, Symptoms, and Impact
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing over 100 different conditions that affect the joints. The two most common
types are osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Osteoarthritis, often referred to as "wear and tear"
arthritis, results from the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. This breakdown leads to bone-on-bone friction,
causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disease
where the body's immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation and damage. This inflammation can
lead to joint deformities and systemic symptoms like fatigue and fever. Both conditions lead to pain, stiffness,
swelling, and reduced range of motion, significantly impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. According
to the World Health Organization, osteoarthritis is a leading cause of disability worldwide.
The impact of arthritis extends beyond physical symptoms. Chronic pain and limited mobility can lead to fatigue,
sleep disturbances, and psychological distress, such as anxiety and depression. Managing arthritis effectively
requires a multidisciplinary approach that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition.
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in this process, helping individuals to maintain or improve their physical function,
manage pain, and learn strategies for coping with the challenges of living with arthritis. The impact of arthritis on
specific activities of daily living, such as dressing, bathing, and cooking, can be significant, leading to a loss of
independence and a reduced quality of life.
Case Study: TENS for Osteoarthritis Pain Relief
Patient Presentation: A Case of Knee Osteoarthritis
Our case study focuses on a 62-year-old female patient, Mrs. A, diagnosed with osteoarthritis in her right
knee. Mrs. A's medical history included no other significant medical conditions, and she was not taking any
other medications. She reported experiencing chronic pain (rated 7/10 on the Visual Analog Scale - VAS) that
significantly limited her ability to walk, climb stairs, and perform household chores. Her condition had been
ongoing for several years, and she had tried various pain medications with limited success and concerns about
side effects. Mrs. A's frustration and desire for a more sustainable solution resonated deeply with our team. A
physical examination revealed swelling, tenderness, and reduced range of motion in her right knee. Specific
measurements showed a limited range of motion of 0-90 degrees of flexion and extension. Her primary goals
were to reduce pain, improve mobility, and regain independence in her daily activities.
Mrs. A's case is representative of many individuals living with osteoarthritis. The chronic pain and functional
limitations associated with the condition can have a profound impact on their lives. Therefore, a comprehensive
treatment plan that addresses both pain management and functional rehabilitation is essential. In Mrs. A's
case, TENS therapy was considered as a non-pharmacological approach to complement her existing treatment
regimen. The chronic pain and functional limitations associated with the condition can have a profound impact
on their lives. Therefore, a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both pain management and functional
rehabilitation is essential.
Personalized TENS Treatment Plan Using Axonease
Following a thorough assessment, a personalized TENS treatment plan was developed for Mrs. A, utilizing the
Axonease device. The plan included the following parameters, based on established guidelines and best practices
in physiotherapy:
• Electrode Placement: Two electrodes were placed around the knee joint, one above and one below the patella,
ensuring optimal coverage of the painful area.
• Frequency: A frequency of 80 Hz was selected, based on evidence suggesting its effectiveness in providing
pain relief for musculoskeletal conditions.
• Pulse Width: A pulse width of 200 microseconds was chosen to stimulate the sensory nerves effectively.
• Intensity: The intensity was gradually increased until Mrs. A reported a comfortable tingling sensation without
any muscle contraction.
• Treatment Duration: Each TENS session lasted for 30 minutes, and she was instructed to use the device twice
daily.
The selection of these parameters was based on established guidelines and best practices in physiotherapy.
The goal was to provide effective pain relief while minimizing any potential side effects. The Axonease device
was chosen for its ease of use, portability, and ability to deliver precise and consistent electrical stimulation. The
physiotherapist educated Mrs. A on how to properly apply the electrodes, adjust the settings, and monitor her skin
for any signs of irritation. The rationale behind selecting 80 Hz frequency was based on its established efficacy
in modulating pain pathways. The 200-microsecond pulse width was chosen to effectively stimulate the sensory
nerves. Alternative electrode placements were considered, but the chosen placement was deemed optimal for
targeting the specific area of pain. The intensity was carefully adjusted based on Mrs. A's feedback, ensuring a
comfortable tingling sensation without muscle contraction.
Observed Outcomes: Tracking Pain Reduction and Function Improvement
After two weeks of consistent TENS therapy, Mrs. A reported a significant reduction in her knee pain, with
her VAS score decreasing from 7/10 to 4/10. She also experienced improved mobility, allowing her to walk
for longer distances and climb stairs with less difficulty. Furthermore, she reported a decrease in her reliance
on pain medication. Objective measurements, such as the Timed Up and Go test, also showed improvement
in her functional performance.
These positive outcomes highlight the potential benefits of TENS therapy for managing osteoarthritis pain and
improving function. The combination of pain reduction and improved mobility allowed Mrs. A to engage more
actively in her daily activities and experience a better quality of life. It is important to note that the effectiveness
of TENS can vary from person to person, and it is not a substitute for other essential components of arthritis
management, such as exercise, weight management, and lifestyle modifications. Mrs. A's subjective experience of
TENS therapy was positive, with her reporting a significant reduction in pain and an improved sense of well-being.
TENS for Arthritis: Benefits, Limitations & Physiotherapy Integration
Benefits of TENS Therapy in Arthritis Management
TENS offers several advantages as a pain management tool for arthritis. It is a non-invasive and drug-free
approach, minimizing the risk of side effects associated with pain medications. It is also portable and can be
used at home, providing convenient and accessible pain relief. Moreover, TENS can be used in conjunction with
other treatments, such as exercise and manual therapy, to enhance overall outcomes.
The benefits of TENS extend beyond pain relief. By reducing pain and improving mobility, TENS can help
individuals with arthritis to participate more fully in their daily activities, maintain their independence, and improve
their overall quality of life. It can also reduce the need for pain medications, which can have significant side effects
and potential for dependence. The cost-effectiveness of TENS therapy, compared to other pain management
options, is also a significant advantage. By reducing pain and improving mobility, TENS can help individuals with
arthritis to participate more fully in their daily activities, maintain their independence, and improve their overall
quality of life. It can also reduce the need for pain medications, which can have significant side effects and potential
for dependence.
Limitations and Considerations
While TENS can be an effective pain management tool, it is not a cure for arthritis. Its effects are often temporary,
and it may not be effective for all individuals. Some people may not experience any pain relief from TENS, while
others may only experience a modest reduction in pain. Additionally, TENS is not recommended for individuals
with certain medical conditions, such as pacemakers or epilepsy. It is important to have realistic expectations
about the potential benefits of TENS and to understand its limitations. TENS should be used as part of a
comprehensive treatment plan that includes other strategies for managing arthritis, such as exercise, weight
management, and lifestyle modifications. It is also essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine
if TENS is appropriate and to receive guidance on its proper use.
Contraindications for TENS therapy include pregnancy, the presence of implanted electronic devices, and certain
skin conditions. Potential side effects, such as skin irritation or muscle soreness, are generally mild and can be
minimized through proper electrode placement and intensity adjustment. Patient education and adherence to the
TENS treatment plan are crucial for optimal outcomes.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Optimizing TENS Therapy
Physiotherapists play a crucial role in optimizing the use of TENS for arthritis pain management. They can conduct
a thorough assessment to determine if TENS is appropriate for an individual and develop a personalized treatment
plan based on their specific needs and goals. Physiotherapists can also educate patients on how to properly use
the TENS device, adjust the settings, and monitor their skin for any signs of irritation. A physiotherapist can help
determine if TENS is appropriate for an individual.
Furthermore, physiotherapists can integrate TENS therapy with other physiotherapy interventions, such as
exercise, manual therapy, and education, to enhance overall outcomes. They can also provide guidance on
lifestyle modifications and self-management strategies to help individuals with arthritis manage their condition
effectively. The expertise of a physiotherapist is essential for ensuring that TENS is used safely and effectively
as part of a comprehensive arthritis management plan.
The role of physiotherapy extends beyond the application of TENS. Physiotherapists address other impairments
associated with arthritis, such as muscle weakness, joint stiffness, and balance problems. They also emphasize a
multidisciplinary approach to arthritis management, involving collaboration between physiotherapists, physicians,
and other healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
This case study demonstrates the potential benefits of TENS therapy as a non-pharmacological
approach to managing arthritis pain. The patient in this case experienced significant pain reduction and improved
function after incorporating TENS into her physiotherapy treatment plan. While TENS is not a cure for arthritis
and may not be effective for everyone, it can be a valuable tool for managing symptoms and improving quality of
life when used appropriately and under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional. TENS can be used
for pain management in India.
If you are living with arthritis pain, consider discussing TENS therapy with your physiotherapist or healthcare
provider. They can help you determine if TENS is right for you and develop a personalized treatment plan to
address your specific needs and goals. Remember, effective arthritis management requires a comprehensive
approach that includes various strategies for pain relief, functional rehabilitation, and lifestyle modifications.
Transforming physiotherapy, one patient at a time.