Shoulder impingement, also known as subacromial impingement, is a common condition that causes shoulder
pain and limits movement, significantly impacting daily activities. Imagine struggling to reach for a shelf, finding it
difficult to play your favorite sport, or even experiencing discomfort while sleeping. Early diagnosis and appropriate
intervention are crucial for optimal outcomes, preventing the potential for chronic pain, limited mobility, and the
need for more invasive treatments. This blog will provide a detailed overview of shoulder impingement, explaining
how Electromyography (EMG) plays a crucial role in diagnosis, and outlining effective physiotherapy treatments
and recovery strategies.
What is Shoulder Impingement? Understanding the Causes and
Symptoms
Shoulder impingement occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles become compressed or irritated
as they pass through the space between the acromion (part of the shoulder blade) and the humerus (upper
arm bone). This compression leads to inflammation, pain, and a reduced range of motion in the shoulder.
Shoulder impingement can develop from several factors, including overusing your shoulder, such as painting a
ceiling or engaging in repetitive throwing motions. Bone spurs, which are bony growths, can also contribute to
impingement. Poor posture, like rounded shoulders or a forward head posture, can exacerbate the condition.
Age-related changes in the shoulder joint and anatomical factors can also predispose individuals to impingement.
Recognizing the causes of shoulder impingement is the first step in managing the condition.
You might experience pain when lifting your arm, reaching behind your back, or even at night. The pain can range
from mild to severe, and early recognition of these symptoms is vital for timely intervention. Specific activities
like reaching overhead or across the body can aggravate the pain. Shoulder pain can significantly impact daily
activities and quality of life. The pain might be a sharp, aching, or dull sensation, potentially radiating down your arm.
EMG for Shoulder Impingement: How it Helps Diagnose Shoul-
der Pain
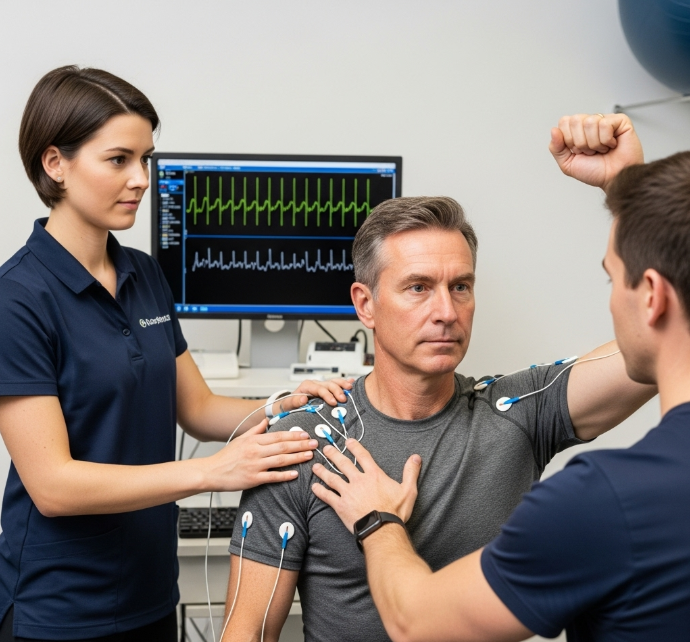
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic test that assesses the health of muscles and the nerve cells (motor
neurons) that control them. In the context of shoulder impingement, EMG helps to rule out other conditions that
may be causing shoulder pain, such as nerve compression or muscle weakness. It can also help identify specific
muscles affected by the impingement.
During an EMG, a small needle electrode is inserted into the muscle to record its electrical activity. The electrical
signals are displayed on a screen, allowing the healthcare professional to assess the muscle's function. The
assessment includes evaluating the amplitude, duration, and frequency of the electrical signals, which provide
insights into the health of the muscle and the nerves that supply it. The patient can expect some discomfort during
the test, but it is generally well-tolerated.
EMG can help differentiate between shoulder impingement and other conditions like rotator cuff tears, bursitis, or
arthritis. While EMG is a helpful tool, it's not always necessary for diagnosing shoulder impingement. It provides
objective data about muscle and nerve function, guiding treatment decisions and monitoring the effectiveness of
interventions. EMG is particularly useful when nerve involvement is suspected, helping to differentiate between
nerve compression and rotator cuff pathology.
Diagnosing Shoulder Impingement: A Multi-faceted Approach
Diagnosing shoulder impingement typically involves a combination of physical examination, patient history, and
imaging studies. A thorough physical examination includes assessing the range of motion, strength, and stability
of the shoulder joint. Specific provocative tests, such as the Hawkins-Kennedy test and the Neer test, can help
identify impingement. These tests involve specific movements designed to reproduce the patient's pain.
To get a clear picture, your healthcare provider will likely combine a physical exam with imaging, such as X-rays
or MRI. X-rays can reveal bone spurs or other structural abnormalities, while MRI provides detailed images of
the soft tissues, including the rotator cuff tendons. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate diagnosis
and the right treatment plan. Diagnostic tests for shoulder impingement are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
As discussed earlier, EMG may be used to assess nerve and muscle function, particularly when nerve compres-
sion or muscle weakness is suspected.
Effective Physiotherapy Treatment Options for Shoulder Impingement
The goals of physiotherapy are to reduce pain and inflammation, restore range of motion, strengthen the rotator
cuff muscles, and improve overall shoulder function. Treatment approaches are conservative, focusing on restoring
normal biomechanics and function.
Common physiotherapy techniques for shoulder impingement include manual therapy, therapeutic exercises,
and modalities such as ultrasound and electrical stimulation. Manual therapy techniques may be used to
improve joint mobility and reduce muscle tension, including joint mobilization and soft tissue release. Therapeutic
exercises focus on strengthening the rotator cuff muscles and improving scapular stability, including rotator cuff
strengthening, scapular stabilization, and range-of-motion exercises.
Specific examples of manual therapy include joint mobilization to restore normal joint movement and soft tissue
release to address muscle tightness. Therapeutic exercises might include rotator cuff strengthening exercises
like external rotation with resistance, scapular stabilization exercises to improve shoulder blade control, and
range-of-motion exercises to restore flexibility. Physiotherapy treatment for shoulder impingement also includes
patient education on proper posture, body mechanics, and activity modification. The use of physioemg devices
can also be incorporated to enhance muscle re-education and provide real-time feedback during exercises.
Shoulder Impingement Rehabilitation: Regaining Strength and
Preventing Recurrence
Shoulder impingement rehabilitation is a crucial phase in the recovery process. It focuses on gradually increasing
the intensity of exercises and activities to restore full function and prevent recurrence.
Rehabilitation involves a carefully planned progression of exercises. You'll start with stretching to improve
flexibility, then move on to strengthening exercises that target the rotator cuff and shoulder blade muscles. Finally,
you'll practice functional movements, like lifting and reaching, to help you confidently return to your daily activities.
Home exercises are essential for maintaining shoulder health and preventing recurrence.
Preventing recurrence of shoulder impingement involves addressing underlying factors such as poor posture,
muscle imbalances, and improper body mechanics. Patients are educated on how to maintain proper posture,
perform exercises regularly, and avoid activities that may aggravate their symptoms. Long-term management
strategies are essential for maintaining shoulder health and preventing future episodes of impingement. Patient
education is key to successful recovery. Addressing any underlying muscle imbalances or biomechanical issues
that may contribute to impingement is also important.
Conclusion
Shoulder impingement is a common condition that can cause significant pain and disability. Early diagnosis and
appropriate treatment are essential for achieving optimal outcomes. EMG plays a valuable role in diagnosing
shoulder impingement and differentiating it from other conditions. Physiotherapy is a cornerstone of treatment,
focusing on pain relief, restoring function, and preventing recurrence.
If you're struggling with shoulder pain, don't wait. Reach out to a qualified healthcare professional for a thorough
evaluation and a personalized plan to get you back on track. We believe that personalized care, powered by
innovation, is the key to unlocking better outcomes and transforming physiotherapy, one patient at a time. Consult
with a physiotherapist for personalized care.